Schedule Google Compute Engine Instances to Save Big Money.
Virtual machine is first type of compute for someone starting with the cloud. As per many reports 80-85% enterprise workload have migrated to cloud.
With this increased cloud adoptions, individuals also thinking of shifting some heavy compute tasks on cloud VMs, rather than building a machine at home. As there is a benefit of pay-as-you-go model in cloud resources and no mainteance required.
In this article I’ll be showing you how you can save up money if you are using compute engine VMs for very few hours a day.
GCP compute engine - pay as you go
With pay-as-you-go model you only pay for time you use a resource.
If you have a schedule like daily for 2-3 hours you will need to use a VM, you can keep it in stopped or suspended state.
GCP compute engine lets you start and stop a compute engine VM. In this case you only pay minor charges for network resources and disk attached. In GCP there is also an option to suspend and resume compute engine VM. Which is similar to hibernate on our physical machines.
NOTE: Right now as I am writing this article, E2 type compute engine instances do not support suspend/resume feature. So I had to choose N2 type VM. So keep this in mind if you want suspend/resume feature for your use-case.
Managing state using cloud scheduler and cloud function
This gcp documentation show how you can use cloud functions along with pub-sub trigger and cloud scheduler to manage state of VM on a cron schedule.
These extra resources are required for this solution
- cloud function - logic to change VM state
- pub-sub - acts as trigger for cloud function
- cloud scheduler - publishes message to pub-sub when cron expression is matched.
VM price for month ranges from 15$-20$ per vCPU. cloud schedulerand pubsub costs 3-4 $ for this use case. This is peanuts amount as compared to VMs monthly cost. Use pricing calculator to calculate exact costs.
Implementation
Cloud function has a pub-sub trigger.
 Cloud function code is as below,
Cloud function code is as below, change_vm_state function is invoked when pub-sub message is received.
import base64
import googleapiclient.discovery
import sys
PROJECT = "GCP-PROJECT-NAME"
ZONE = "VM-ZONE"
INSTANCE = "INSTANCE-NAME"
def suspend(compute):
return compute.instances().suspend(project=PROJECT, zone=ZONE, instance=INSTANCE).execute()
def resume(compute):
return compute.instances().resume(project=PROJECT, zone=ZONE, instance=INSTANCE).execute()
def change_vm_state(event, context):
# Parse pubsub message
pubsub_message = base64.b64decode(event['data']).decode('utf-8')
# Pubsub message should not be empty
if pubsub_message == None:
print("No operation specified, choose either `suspend` or `resume`")
sys.exit()
# Create compute client using googleapiclient.
# Suspend resume comes under beta APIs, so we need to pass `compute` and `beta` params.
compute = googleapiclient.discovery.build('compute', 'beta')
if pubsub_message == "suspend":
suspend(compute)
elif pubsub_message == "resume":
resume(compute)
else:
print("Invalid operation. choose either `suspend` or `resume`")
sys.exit()
This scripts require google-api-python-client==1.10.0 library as dependancy.
We need to reference the beta APIs using this library.
Read more on GCP beta APIs here.
Keep in mind that you have to attach a service account which has compute engine permissions to start/stop/suspend/resume VM.
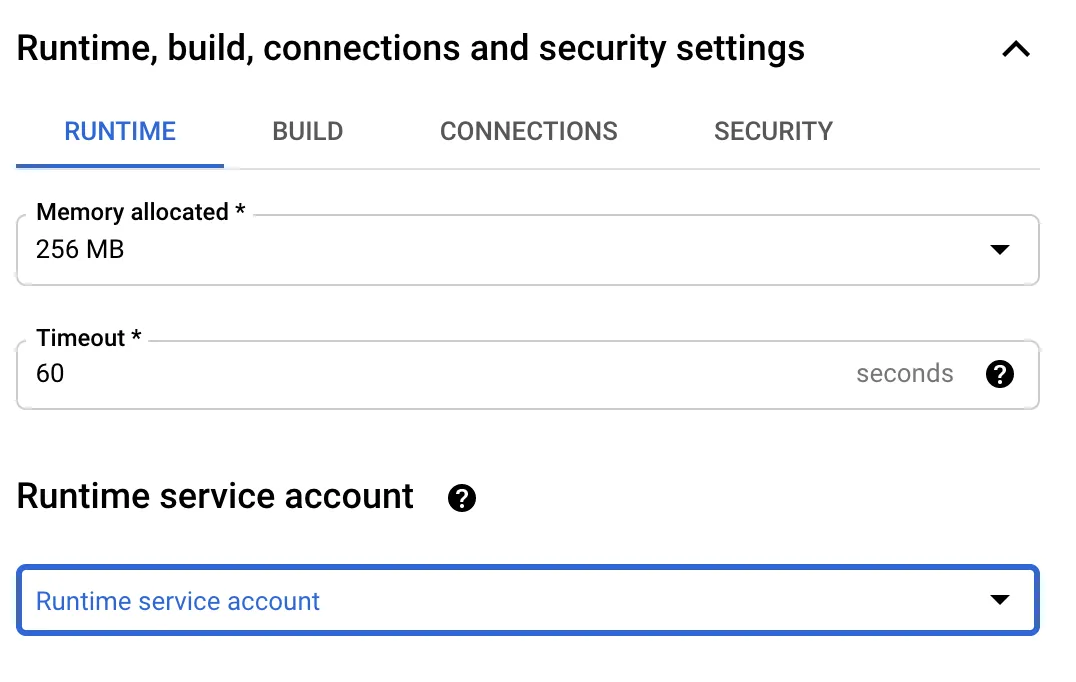
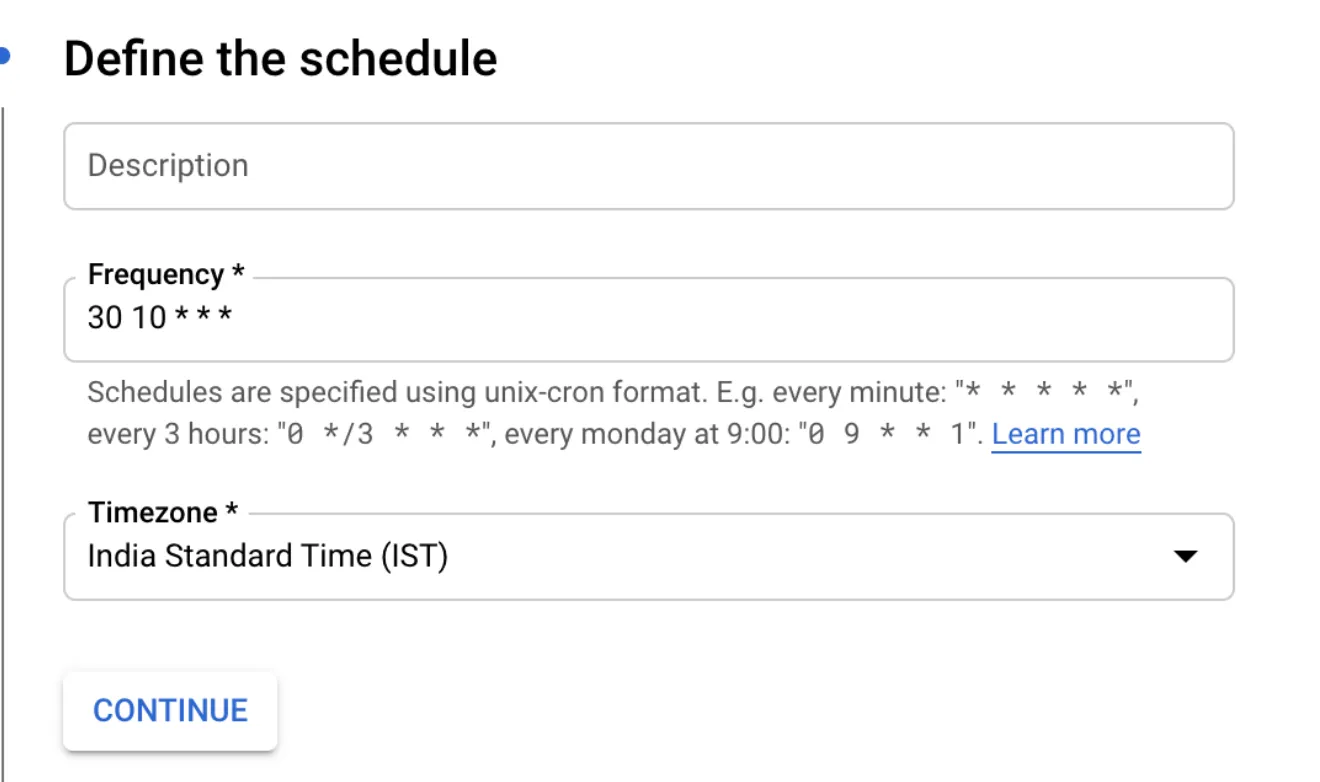
Using cloud scheduler you can send a message to pubsub on a cron schedule.
In next step you can define what message to send to pub-sub.
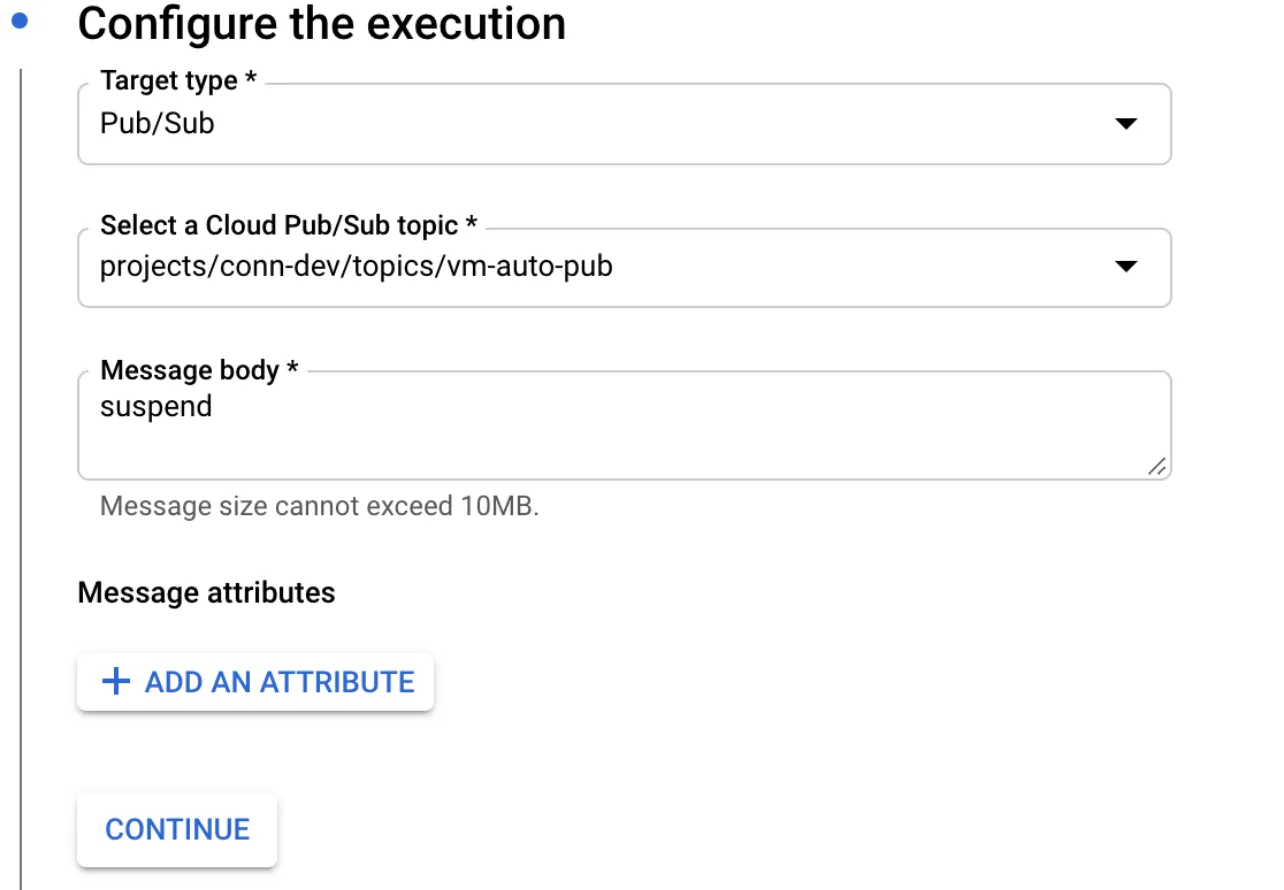
This way you dont have to remember to suspend the VM when you are done working. 